Recent studies have revealed the widespread presence of Forever Chemicals in bottled and tap water around the world, raising significant concerns about public health and water safety. These toxic substances, known scientifically as per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), are termed Forever Chemicals because they do not break down in nature and can accumulate over time, posing long-term risks to human health. This article delves into what Forever Chemicals are, how they enter our water systems, their effects, and what measures can be taken to reduce exposure.

What Are Forever Chemicals and Why Are They Dangerous?
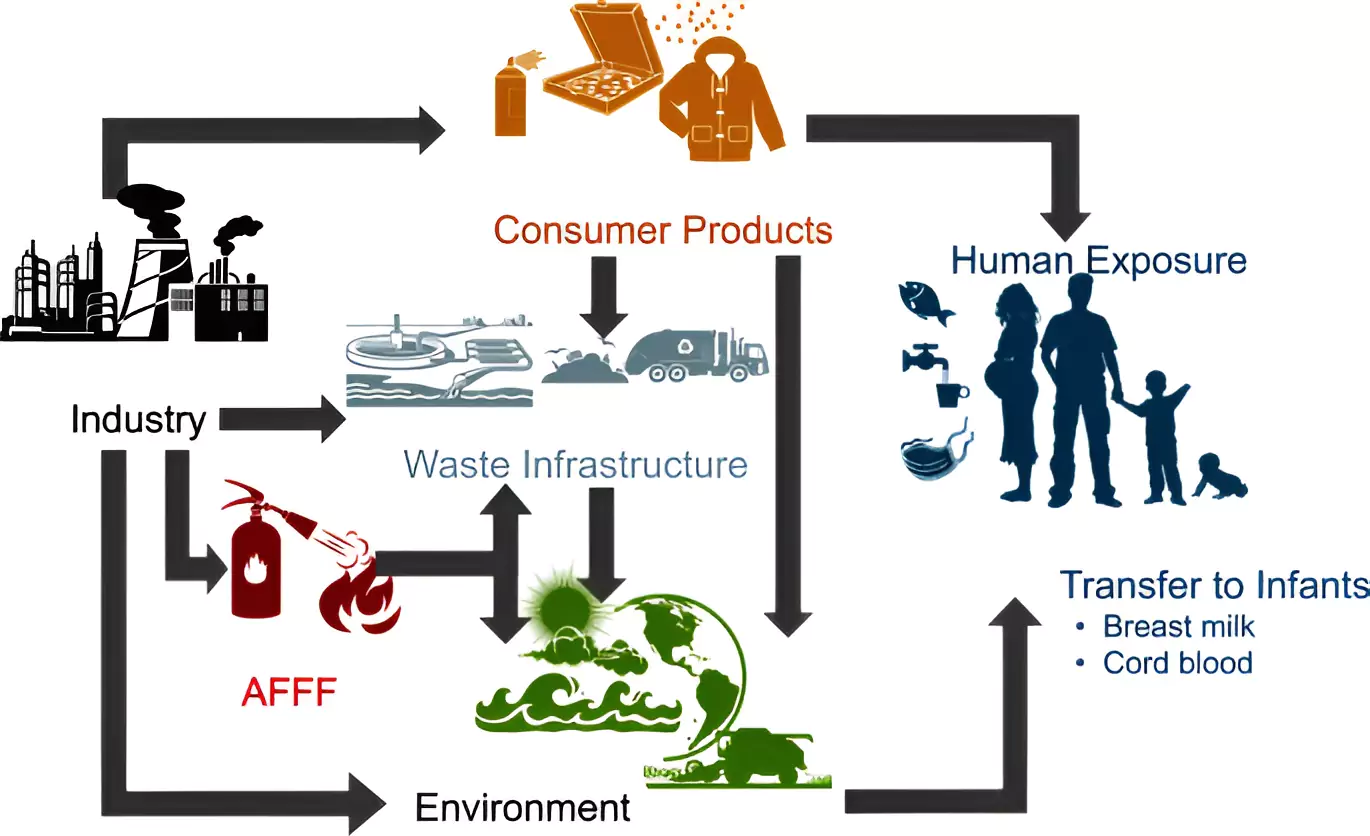
Forever Chemicals are a group of man-made chemicals that have been widely used in various industries and consumer products, including waterproof clothing, fire-fighting foams, and non-stick cookware. The unique properties of Forever Chemicals—such as their resistance to water, oil, and heat—make them highly useful in manufacturing. However, these same properties also make them incredibly persistent in the environment.
The most alarming characteristic of Forever Chemicals is their inability to break down naturally, leading to their accumulation in soil, water, and living organisms. Once these chemicals enter the human body—whether through inhalation, ingestion of contaminated food or water, or absorption through the skin—they remain there for extended periods, causing a range of health issues. Studies have linked Forever Chemicals to impaired immune function, liver damage, decreased birth weight, and even cancer.
Forever Chemicals Found in Global Water Supplies: The Shocking Discovery
A new study has revealed that Forever Chemicals are present in bottled and tap water samples collected from around the world. Researchers found that 10 different PFAS compounds were detected in water from major cities in the UK and China. In some cases, concentrations of these chemicals were alarmingly high.
For example, bottled water sourced from 15 countries showed traces of PFAS, with perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) being detected in over 99% of the samples. The discovery of these Forever Chemicals in drinking water underscores the global scale of this problem and highlights the urgent need for stricter regulations and monitoring.
Why Forever Chemicals Are So Common in Drinking Water
One of the primary reasons Forever Chemicals are found in drinking water is their widespread industrial use. PFAS are used in a variety of products, from waterproof clothing to non-stick cookware and food packaging. Over time, these chemicals leach into the environment, contaminating water sources.
Additionally, Forever Chemicals are used in fire-fighting foams, particularly in airports and industrial sites. When these foams are deployed, they can seep into the ground and contaminate nearby water supplies. Once in the water system, Forever Chemicals are incredibly difficult to remove, making them a persistent threat to drinking water safety worldwide.
Forever Chemicals in Bottled Water: Is It Safer Than Tap Water?
Many consumers turn to bottled water as a safer alternative to tap water, assuming that it is more purified. However, the recent study challenges this assumption, revealing that Forever Chemicals are present in both bottled and tap water. While natural mineral water was found to have higher concentrations of PFAS compared to purified water, the contamination levels in most bottled waters were still within the health advisory limits set by regulatory agencies.
Interestingly, the study found no significant difference in Forever Chemicals concentrations between glass and plastic bottles, or between still and sparkling water. This finding suggests that consumers cannot rely on bottled water alone to avoid exposure to PFAS.
Health Risks Associated with Forever Chemicals
The health risks posed by Forever Chemicals are substantial. These substances have been linked to a wide range of adverse health effects, including:
- Lowered immune response: Exposure to Forever Chemicals can weaken the body’s immune system, reducing its ability to fight off infections and lowering the effectiveness of vaccines.
- Impaired liver function: PFAS can accumulate in the liver, leading to potential liver damage over time.
- Increased cancer risk: Some studies have shown a correlation between high PFAS exposure and an increased risk of certain cancers, such as kidney and testicular cancer.
- Reproductive issues: Pregnant women exposed to Forever Chemicals have reported decreased birth weights and other complications.
Given the long-term health implications, it is critical to reduce exposure to Forever Chemicals, especially through drinking water.
How to Reduce Exposure to Forever Chemicals in Water
While Forever Chemicals are pervasive, there are steps that individuals can take to minimize their exposure, particularly in drinking water. One of the simplest and most effective methods is using water filtration systems, such as activated carbon filters, which can significantly reduce PFAS concentrations. According to the study, filtration methods can remove up to 90% of these harmful substances from drinking water, depending on the treatment type.
Additionally, boiling water can also help to reduce the levels of certain Forever Chemicals, though it may not be as effective for all PFAS compounds. Regular monitoring of water quality, combined with the use of filtration systems, can provide a practical solution for minimizing the health risks associated with Forever Chemicals.
Regulatory Action Needed to Combat Forever Chemicals
Despite growing awareness of the dangers posed by Forever Chemicals, regulatory action remains inconsistent across different countries. While some governments have banned certain PFAS compounds, others continue to allow their use in various industries. The lack of global regulation makes it difficult to fully control the spread of Forever Chemicals in the environment.
Stricter regulations and international cooperation are crucial to tackling this issue. Governments need to enforce stricter limits on PFAS in drinking water and ensure that industries adopt safer alternatives to Forever Chemicals. Ongoing monitoring and public awareness campaigns will also play a vital role in reducing exposure.
Conclusion: Forever Chemicals in Water—A Global Health Concern
The presence of Forever Chemicals in bottled and tap water highlights the urgency of addressing this global health issue. These persistent chemicals pose long-term risks to human health, and their widespread contamination of water supplies underscores the need for immediate action. While filtration and boiling methods can help reduce exposure, stricter regulations and more effective treatment solutions are essential to safeguarding public health. As more research on Forever Chemicals emerges, it is critical that governments, industries, and consumers work together to mitigate this growing threat.

