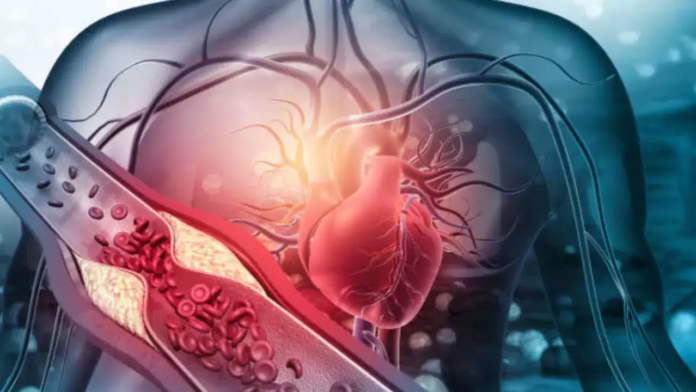
Atherosclerosis, often referred to as the “silent killer,” is a progressive condition that narrows and hardens arteries due to the buildup of plaques composed of cholesterol, fat, and other substances. This condition is dangerous because it often develops unnoticed over years, with minimal or no symptoms until it leads to severe complications such as heart attacks, strokes, or peripheral artery disease.
Understanding Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a cardiovascular condition where plaques form along the walls of arteries, causing them to lose their elasticity and narrowing the blood flow. Over time, these plaques may rupture, triggering blood clots that can completely block blood flow to vital organs like the heart and brain.
Dr. Saurabh Juneja, a CTVS surgeon, emphasizes that atherosclerosis progresses silently and is often detected only after significant damage has occurred.
Why It’s Called the ‘Silent Killer’?
- Asymptomatic Nature:
Atherosclerosis often lacks noticeable symptoms in its early stages, making it difficult to diagnose without specific tests. - Gradual Progression:
The condition progresses slowly over decades, with symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, or fatigue appearing only when the arteries are severely blocked. - Life-Threatening Complications:
By the time symptoms manifest, the patient may already be at risk of severe cardiovascular events, including heart attacks or strokes, which can be fatal if not promptly treated.
Risk Factors for Atherosclerosis
Several factors contribute to the development and progression of atherosclerosis:
- High Cholesterol: Elevated LDL (bad cholesterol) levels increase plaque buildup.
- Smoking: Damages the lining of arteries, making them more prone to plaque formation.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels contribute to arterial damage and inflammation.
- Hypertension: Puts extra stress on arterial walls, accelerating plaque formation.
- Obesity: Associated with higher cholesterol levels and increased risk of inflammation.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of exercise contributes to poor cardiovascular health.
Common Symptoms and Signs
In advanced stages, atherosclerosis can lead to the following symptoms:
- Angina (Chest Pain): Caused by reduced blood flow to the heart.
- Shortness of Breath: Due to insufficient oxygen supply.
- Fatigue: Common in cases of blocked arteries.
- Leg Pain: Particularly when walking, indicating peripheral artery disease.
- Stroke Symptoms: Sudden weakness, speech difficulty, or facial drooping due to blocked blood flow to the brain.
How Atherosclerosis Is Diagnosed?
Early detection is critical to managing atherosclerosis and preventing severe complications. Diagnostic methods include:
- Blood Tests: To measure cholesterol and blood sugar levels.
- Imaging Tests: CT scans, MRIs, or ultrasounds to visualize arteries.
- Angiography: A procedure to examine arterial blockages.
- Stress Tests: To assess heart function under physical exertion.
Treatment Options
Once diagnosed, atherosclerosis can be managed and treated through a combination of medical and lifestyle interventions:
- Medications:
- Statins: Lower cholesterol levels and prevent plaque buildup.
- Antihypertensives: Control blood pressure.
- Antiplatelets: Prevent blood clot formation.
- Surgical Procedures:
- Angioplasty: Opens up blocked arteries using a stent.
- Bypass Surgery: Creates an alternate route for blood flow around blocked arteries.
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Dietary Modifications: A heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
- Regular Exercise: Improves cardiovascular health and helps manage weight.
- Smoking Cessation: Reduces arterial damage.
- Stress Management: Lowers risk factors like high blood pressure.
Preventing Atherosclerosis
The best way to combat the silent killer is through prevention:
- Maintain a healthy diet low in saturated fats and cholesterol.
- Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity weekly.
- Regularly monitor blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques like yoga and meditation.
A Call for Early Detection
The silent and progressive nature of atherosclerosis makes regular health check-ups essential. Early detection and intervention can save lives, reduce the risk of severe cardiovascular events, and improve overall health outcomes. Recognizing subtle symptoms and adopting a proactive approach to heart health is the key to preventing this silent killer from taking a heavy toll.