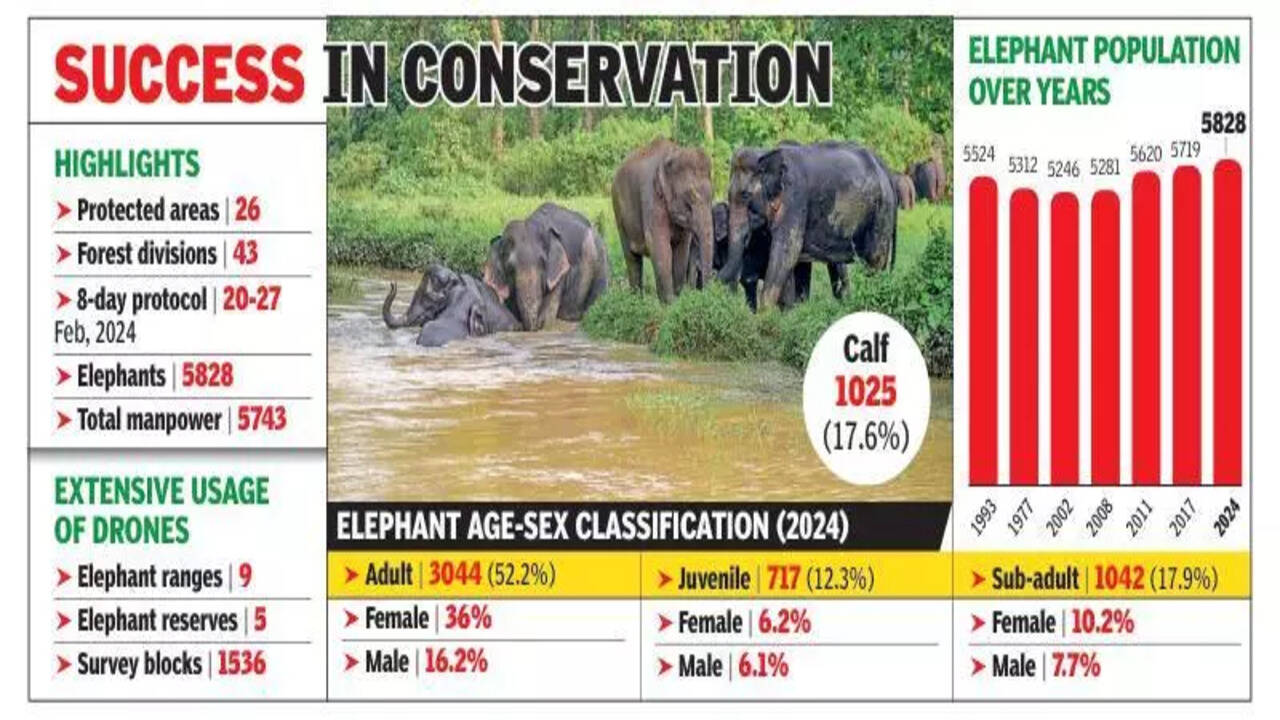
Assam Elephant Population has reached 5,828, as revealed in the Elephant Population Estimation 2024 conducted by the state forest department. This marks a modest increase from the 2017 estimation, which recorded 5,719 elephants. The comprehensive survey was conducted across all 43 forest divisions in Assam and provides a detailed breakdown of the population demographics, including 3,044 adults, 1,042 sub-adults, 717 juveniles, and 1,025 calves.
A notable 82% of the total elephant population—4,777 elephants—reside within the state’s five elephant reserves, with the Chirang-Ripu Elephant Reserve showing the highest density.
Assam Elephant Population Trends Over The Years
Assam’s elephant population has shown remarkable stability over the decades, despite significant environmental challenges. Historical data reveals a population of 5,620 elephants in 2011, 5,281 in 2008, and 5,246 in 2002. The latest estimation reflects a continuing upward trend, reinforcing the success of conservation efforts in the state.
According to a statement by the Principal Chief Conservator of Forests, Wildlife, and Chief Wildlife Warden of Assam, the elephant population has consistently remained above 5,200 despite challenges such as habitat fragmentation, human-elephant conflict, and urbanization.
This steady growth highlights the importance of conservation measures implemented within Assam’s elephant reserves, which serve as critical habitats for the species.

Conservation Efforts And Challenges
The increase in Assam Elephant Population is a testament to the state’s robust conservation strategies. Elephant reserves like Kaziranga-Karbi Anglong, Chirang-Ripu, and Dehing-Patkai provide safe havens for the species, ensuring their protection against poaching and habitat destruction.
However, challenges persist. Human-elephant conflicts remain a significant concern, often arising from habitat encroachment and fragmented forests. Elephants, driven by the need for food and space, sometimes venture into human settlements, leading to conflicts that can result in casualties on both sides.
To address these issues, Assam’s forest department has implemented strategies such as creating elephant corridors, installing barriers, and educating local communities about coexistence. The department has also employed technology, including GPS tracking and drones, to monitor elephant movements and mitigate conflicts.
Focus On The Chirang-Ripu Elephant Reserve
Among the five elephant reserves in Assam, the Chirang-Ripu Elephant Reserve stands out for its high population density. Located in western Assam, this reserve provides an ideal habitat with abundant food and water sources.
The reserve’s success in sustaining a significant portion of the state’s elephant population underscores the effectiveness of targeted conservation efforts. It also highlights the importance of preserving and expanding such protected areas to accommodate the growing elephant population.
Human-Elephant Conflict: A Growing Concern
Despite the positive trends in population growth, human-elephant conflict remains a pressing issue in Assam. Rapid urbanization, agricultural expansion, and infrastructure development have resulted in shrinking habitats for elephants, forcing them to traverse human-dominated landscapes.
Instances of crop raiding and property damage by elephants are common, often leading to retaliatory actions by affected communities. The state has been proactive in addressing these issues by establishing compensation schemes for farmers, promoting community-based conservation initiatives, and encouraging the creation of elephant-friendly agricultural practices.
The government has also prioritized the establishment of elephant corridors, which are crucial for enabling safe migration between fragmented habitats. Such measures aim to reduce conflict while ensuring the long-term survival of Assam’s elephants.
Assam’s Role In India’s Elephant Conservation
Assam plays a vital role in India’s elephant conservation efforts, being home to one of the largest elephant populations in the country. The state’s dense forests and extensive elephant reserves make it a critical stronghold for the species.
Assam’s conservation success serves as a model for other states grappling with similar challenges. The integration of scientific methods, community involvement, and policy measures has been pivotal in maintaining the stability of the elephant population.
As India moves forward with its National Elephant Action Plan, Assam’s experiences and strategies will likely play a significant role in shaping nationwide conservation efforts.
Future Of Elephant Conservation In Assam
The steady growth in Assam Elephant Population is a positive indicator of the state’s commitment to wildlife conservation. However, sustaining this growth requires continued focus on mitigating human-elephant conflicts, expanding protected areas, and fostering greater community involvement in conservation initiatives.
With the ongoing efforts of the forest department and support from local communities, Assam is well-positioned to ensure a thriving future for its elephants while balancing the needs of its human population. The 2024 estimation reaffirms the importance of collective action in preserving one of India’s most iconic species.

