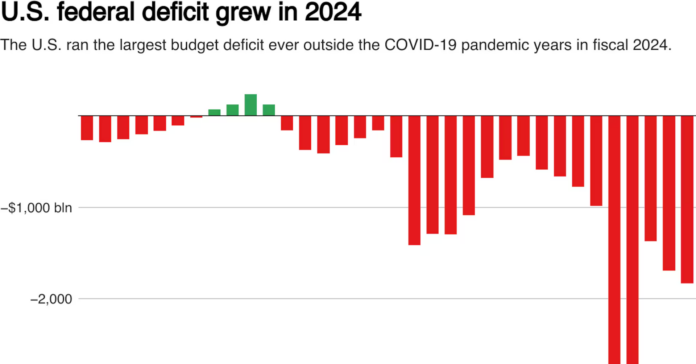
The United States’ financial health took a serious hit in fiscal year 2024, with the budget deficit rising to a staggering $1.83 trillion—the third-largest deficit in the country’s history. This marks a major red flag for economists and policymakers, as it follows the pandemic-induced deficit spikes of the last few years. While the COVID-19 emergency may be behind us, the financial repercussions continue to cast a shadow over the nation. But the real question on everyone’s mind is: What does this mean for the future of America’s economy?
The surge in the deficit was largely driven by the swelling interest payments on federal debt, which, for the first time in US history, crossed the trillion-dollar mark. The government has been grappling with ballooning federal debt, and these interest payments are becoming an increasingly burdensome aspect of the national budget. Add to this the rising costs of Social Security, healthcare, and military spending, and you have a perfect storm of fiscal challenges that the US government must face.
Is the US Headed for an Economic Crisis?
Many financial experts are sounding the alarm bells, warning that the US may be heading toward a financial crisis if this trend continues. The staggering budget deficit signals a dangerous imbalance between government spending and revenue generation, which could lead to more borrowing and, consequently, higher interest payments. The government’s reliance on borrowing is becoming unsustainable, with interest on debt alone consuming a significant chunk of the national budget.

Why Is This Happening?
The US budget deficit in FY24 is a result of multiple factors converging at once. While the COVID-19 pandemic required massive government spending, the aftermath has left lasting effects on the economy. Interest payments on the national debt have soared due to a combination of the increasing debt load and rising interest rates. The Federal Reserve’s efforts to control inflation by hiking interest rates have indirectly contributed to the federal government’s financial strain.
At the same time, entitlement programs such as Social Security and Medicare are eating up larger portions of the budget. With an aging population, the demands on these programs are only expected to grow, putting further pressure on the federal budget.
What Does This Mean for the Average American?
While these numbers may seem abstract to the average American, the consequences are very real. If the government is forced to continue borrowing at this rate, it may have to make tough decisions on spending cuts or raising taxes to manage the debt. Programs like Social Security, healthcare, and infrastructure could see reductions in funding, which would directly affect millions of Americans.
Moreover, high deficits tend to put upward pressure on inflation. With interest rates already high and inflation still a concern, this could lead to even higher costs of living for ordinary Americans. At a time when many households are already struggling with rising prices, this fiscal situation may worsen their financial burden.
The Growing Concern Over Debt
The US national debt has been steadily increasing for years, and it is now approaching $34 trillion. While some argue that deficits are not inherently bad—especially during times of crisis—the scale of borrowing and the cost of servicing this debt are becoming increasingly alarming. High levels of national debt can lead to slower economic growth, higher inflation, and reduced investor confidence in the long term.
One of the biggest concerns is that, as the national debt grows, the government’s ability to respond to future crises—whether economic, military, or healthcare-related—becomes limited. With so much of the budget already committed to paying off past debts, there is less room for maneuver in the face of new challenges.
Is There a Way Out?
Many policymakers and economists are calling for a reassessment of the federal budget. Some are urging for spending cuts, particularly in non-essential areas, while others are advocating for tax reforms that could boost government revenues. However, finding the right balance between spending and taxation is a contentious issue, and there is no easy solution.
Reducing the deficit will require tough choices, including reforms to entitlement programs like Social Security and Medicare, which account for a significant portion of federal spending. However, these programs are politically sensitive, and any attempt to reduce benefits or eligibility could face fierce resistance from the public and politicians alike.
What’s Next for the US Economy?
The situation is dire, but not yet unmanageable. The government must take action to address the growing deficit before it spirals out of control. A combination of spending cuts, tax reforms, and a more strategic approach to managing the national debt could help stabilize the situation. However, these measures will require political will and public support—both of which may be in short supply.
As the US continues to navigate these turbulent economic waters, one thing is clear: the days of unchecked government spending may soon come to an end. Whether the government can find a sustainable path forward remains to be seen, but the stakes could not be higher for the future of America’s economy.